PATIENT PORTAL
Pay My Bill
NON-SURGICAL SERVICES
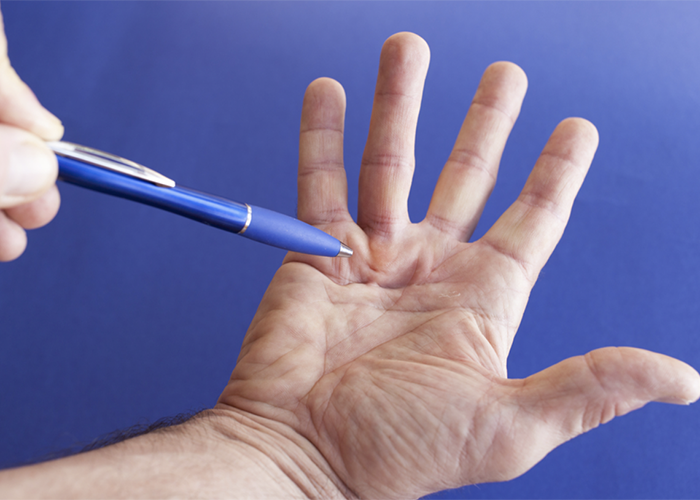
XIAFLEX Injection is a treatment option for Dupuytrens contracture, a condition that affects the hand and fingers. Dupuytrens contracture occurs when the fibrous tissue in the palm thickens and forms nodules or cords, restricting finger movement. XIAFLEX is composed of a unique enzyme called collagenase that helps break down the excess collagen in the hand, allowing for improved hand function.
The injection is administered directly into the affected area by a healthcare professional. This minimally invasive procedure typically takes about 15 minutes and is performed in an outpatient setting. Following the injection, the patient undergoes a series of finger manipulations to help further break down the collagen and straighten the fingers. Over the course of several weeks, the affected tissues gradually dissolve, resulting in improved finger movement. XIAFLEX Injection has proven to be an effective and safe treatment option for Dupuytrens contracture, providing patients with relief from the symptoms and allowing them to regain functional use of their hand and fingers.
The injection is administered directly into the affected area by a healthcare professional. This minimally invasive procedure typically takes about 15 minutes and is performed in an outpatient setting. Following the injection, the patient undergoes a series of finger manipulations to help further break down the collagen and straighten the fingers. Over the course of several weeks, the affected tissues gradually dissolve, resulting in improved finger movement. XIAFLEX Injection has proven to be an effective and safe treatment option for Dupuytrens contracture, providing patients with relief from the symptoms and allowing them to regain functional use of their hand and fingers.
Percutaneous Needle Release is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat Dupuytren’s contracture, a condition characterized by the thickening and contraction of the tissue in the palm of the hand. This condition can cause the fingers to bend inward, limiting their range of motion and hindering daily activities.
During the procedure, a small needle is inserted into the hand to puncture and break up the thickened tissue bands that are causing the contracture. The needle is guided by ultrasound to ensure precision and accuracy. This technique allows for the release of the contracted tissue without the need for a large incision or open surgery.
One advantage of percutaneous needle release is its shorter recovery time compared to traditional surgical methods. Typically, patients are able to resume light activities within a few days and full use of the hand is regained within a few weeks. This procedure offers a less invasive alternative for patients with Dupuytren’s contracture, allowing them to regain functionality.
Ultrasound-guided aspirations refer to a medical procedure where a healthcare professional inserts a needle into a specific body site under the guidance of ultrasound imaging. This technique provides real-time visualization and allows for accurate targeting of the desired area. It is commonly used for the purpose of obtaining tissue or fluid samples for diagnostic purposes.
The procedure is particularly valuable in cases where the target site is deep within the body or when it is difficult to locate by palpation alone. By using ultrasound guidance, healthcare providers can directly visualize the needles position as it is advanced towards the target, ensuring precision and reducing the risk of damage to surrounding structures.
Ultrasound-guided aspirations are commonly performed in various medical specialties, including radiology, oncology, and rheumatology. It has proven to be a safe and effective method in diagnosing various conditions, such as cancers, infections, and fluid collections. Overall, ultrasound-guided aspirations have revolutionized diagnostic medicine, providing a minimally invasive approach that improves accuracy, reduces complications, and enhances patient care.
The procedure is particularly valuable in cases where the target site is deep within the body or when it is difficult to locate by palpation alone. By using ultrasound guidance, healthcare providers can directly visualize the needles position as it is advanced towards the target, ensuring precision and reducing the risk of damage to surrounding structures.
Ultrasound-guided aspirations are commonly performed in various medical specialties, including radiology, oncology, and rheumatology. It has proven to be a safe and effective method in diagnosing various conditions, such as cancers, infections, and fluid collections. Overall, ultrasound-guided aspirations have revolutionized diagnostic medicine, providing a minimally invasive approach that improves accuracy, reduces complications, and enhances patient care.
ULTRASOUND-GUIDED JOINT & TENDON INJECTIONS
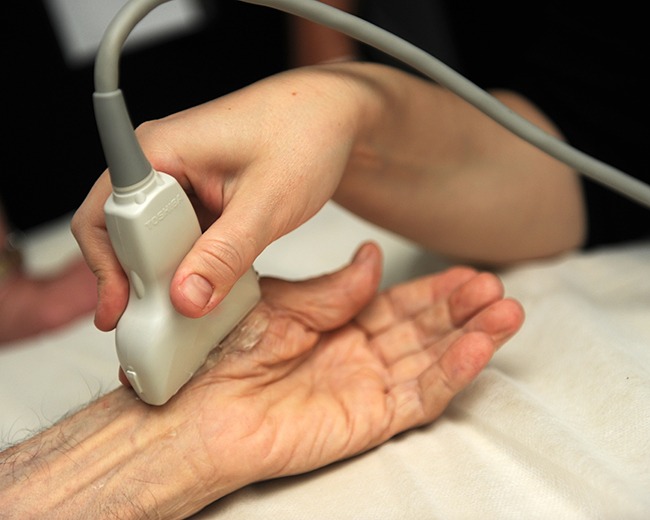
Ultrasound-guided joint and tendon injections are advanced medical procedures used to accurately deliver medications, such as corticosteroids or local anesthetics, to specific areas of the body. This technique involves the use of high-frequency sound waves to create real-time images of the targeted joint or tendon. By providing a visual map of the anatomy, ultrasound guidance ensures precise needle placement, increasing the efficacy and safety of the injection. Additionally, this method allows healthcare professionals to visualize the surrounding structures, including blood vessels and nerves, reducing the risk of potential complications.
Ultrasound-guided joint and tendon injections are commonly used in the treatment of various conditions, including arthritis, tendinitis, and bursitis. They offer several advantages over traditional blind injections, such as improved accuracy, reduced pain, and better patient outcomes. With real-time imaging, practitioners can specifically target the affected area and tailor treatment to the patients individual needs. Overall, ultrasound-guided joint and tendon injections are essential tools in modern medicine, enhancing the accuracy and precision of therapeutic interventions. - Foreign body removal
Ultrasound-guided joint and tendon injections are commonly used in the treatment of various conditions, including arthritis, tendinitis, and bursitis. They offer several advantages over traditional blind injections, such as improved accuracy, reduced pain, and better patient outcomes. With real-time imaging, practitioners can specifically target the affected area and tailor treatment to the patients individual needs. Overall, ultrasound-guided joint and tendon injections are essential tools in modern medicine, enhancing the accuracy and precision of therapeutic interventions. - Foreign body removal
Fracture reduction and casting is a crucial method used in orthopedics to treat bone fractures. This procedure involves repositioning the broken bone fragments, known as reduction, followed by immobilizing the injured area using a cast. Fracture reduction aims to restore normal alignment and length of the fractured bone, promoting proper healing and function. It can be achieved through closed reduction, which involves manipulation of the fracture fragments externally, or open reduction, where surgery is required to align the bones. Once the reduction is achieved, casting is performed to provide stability and support to the fractured bone.
Casting involves the application of a rigid or semi-rigid external dressing, commonly made of plaster or fiberglass. The cast holds the reduced bone in place, prevents further movement, and allows for the natural healing process to occur. It also provides protection to the injured area, reduces pain and swelling, and promotes proper bone alignment. Fracture reduction and casting is a widely used and effective technique in the management of bone fractures, enabling patients to regain mobility and resume their normal activities.
Casting involves the application of a rigid or semi-rigid external dressing, commonly made of plaster or fiberglass. The cast holds the reduced bone in place, prevents further movement, and allows for the natural healing process to occur. It also provides protection to the injured area, reduces pain and swelling, and promotes proper bone alignment. Fracture reduction and casting is a widely used and effective technique in the management of bone fractures, enabling patients to regain mobility and resume their normal activities.
PLASMA-RICH PROTEIN (PRP) INJECTIONS
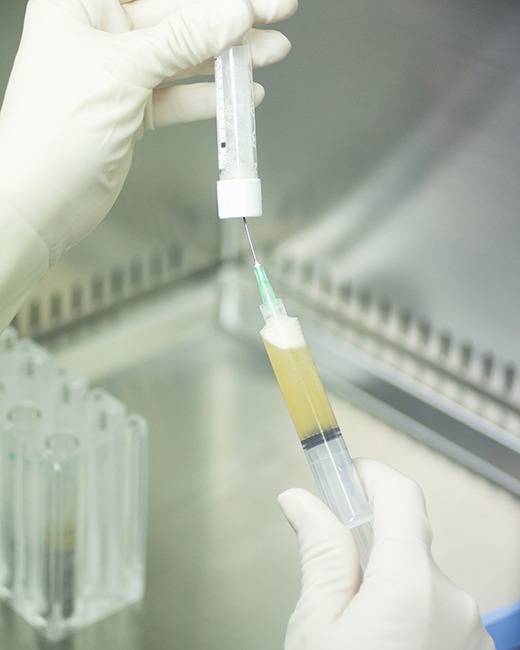
Many patients suffer from tendon and joint disorders. An important aspect of treatment often includes restoring blood flow and allowing the body to more naturally heal itself. A key component of this is Platelet-Rich Plasma therapy, or PRP.
PRP therapy is an injection of a concentrated amount of a patient’s own platelets, which contain growth factors and inflammatory mediators that stimulate angiogenesis (new blood vessel formation) and healing of chronic conditions. This process is done in about 15-20 minutes, and involves drawing a small amount of blood from the patient, placing the sample in a centrifuge to separate the desired platelet concentration, and then performing a tendon or joint injection with the concentrated solution.
Conditions such as elbow tendonitis, rotator cuff disease, hand and wrist tendonitis, and osteoarthritis can be successfully treated with PRP injections. While many insurances provide coverage for PRP therapy, some do not.
For more information about PRP, click Orthobiologics & PRP
PRP therapy is an injection of a concentrated amount of a patient’s own platelets, which contain growth factors and inflammatory mediators that stimulate angiogenesis (new blood vessel formation) and healing of chronic conditions. This process is done in about 15-20 minutes, and involves drawing a small amount of blood from the patient, placing the sample in a centrifuge to separate the desired platelet concentration, and then performing a tendon or joint injection with the concentrated solution.
Conditions such as elbow tendonitis, rotator cuff disease, hand and wrist tendonitis, and osteoarthritis can be successfully treated with PRP injections. While many insurances provide coverage for PRP therapy, some do not.
For more information about PRP, click Orthobiologics & PRP
CALL THE OFFICE
BACK TO THE TOP
CONTACT US
Email checked during normal business hours.